How to Select and Size Irrigation Pump: LEO Step-by-Step Guide
2024.08.16

Choosing the right irrigation pump is crucial for efficient water movement and long-term cost savings. But how do you do it? In this article, we will guide you through the process step-by-step, using examples to clarify each point. By the end, you’ll have the knowledge and confidence to select the best pump for your irrigation system, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.

Key Elements for Selecting the Right Irrigation Pump
With numerous pump types and a wealth of technical information, choosing the right irrigation pump can feel overwhelming. However, understanding a few basic principles makes the process much simpler than it seems. Let's break down the major elements to help you easily grasp the necessary calculations and confidently select the perfect pump for your needs.
a. The Purpose of Using Pumps for Irrigation
Above all, we shall know the reason of using water pumps for irrigation. Simply, the primary purpose of these pumps is to adjust the flow and/or pressure of the system to ensure:
- Adequate flow to feed the largest area
- Sufficient pressure to power every sprinkler head effectively
By managing these factors, pumps help optimize irrigation performance and efficiency.
b. Understanding Key Hydraulic Measurements for Pumps
When selecting a pump, it's crucial to understand two key hydraulic measurements commonly used in pump terminology. These measurements, though their units might vary by market, are:
- Flow Rate (Q): This measures the volume of water the pump can move, typically expressed in gallons per minute (GPM), liters per second (l/s), or cubic meters per hour (m³/h).
- Water Pressure (P): This indicates the force the pump exerts, often measured in pounds per square inch (PSI) or in terms of head height (feet or meters).
The amount of water you need to move and the distance it must travel directly affect the pump's flow and pressure requirements. To ensure optimal performance, select a pump that meets the specific needs of your irrigation system, considering factors like pipe size, sprinkler type, nozzle design, zone size, and layout (usually, they are easier to get by introduction or manufacturers).
Additionally, be aware of the following pressure-related factors:
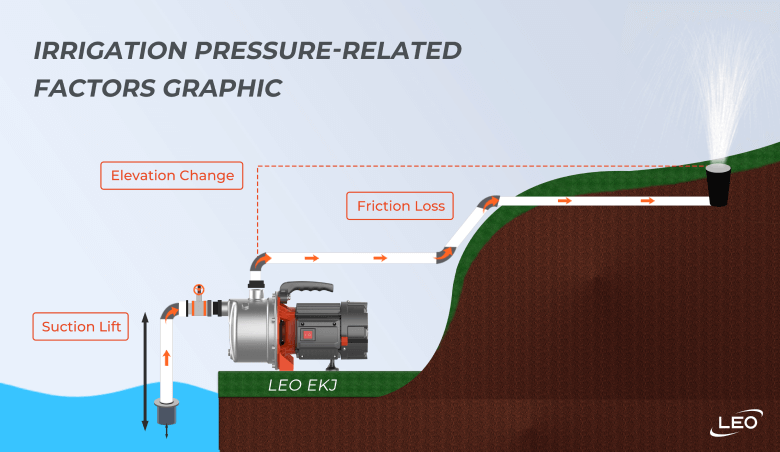
Elevation Change: The vertical distance between the pump and the highest point in your system.
Suction Lift: The vertical distance between the pump inlet and the water source.
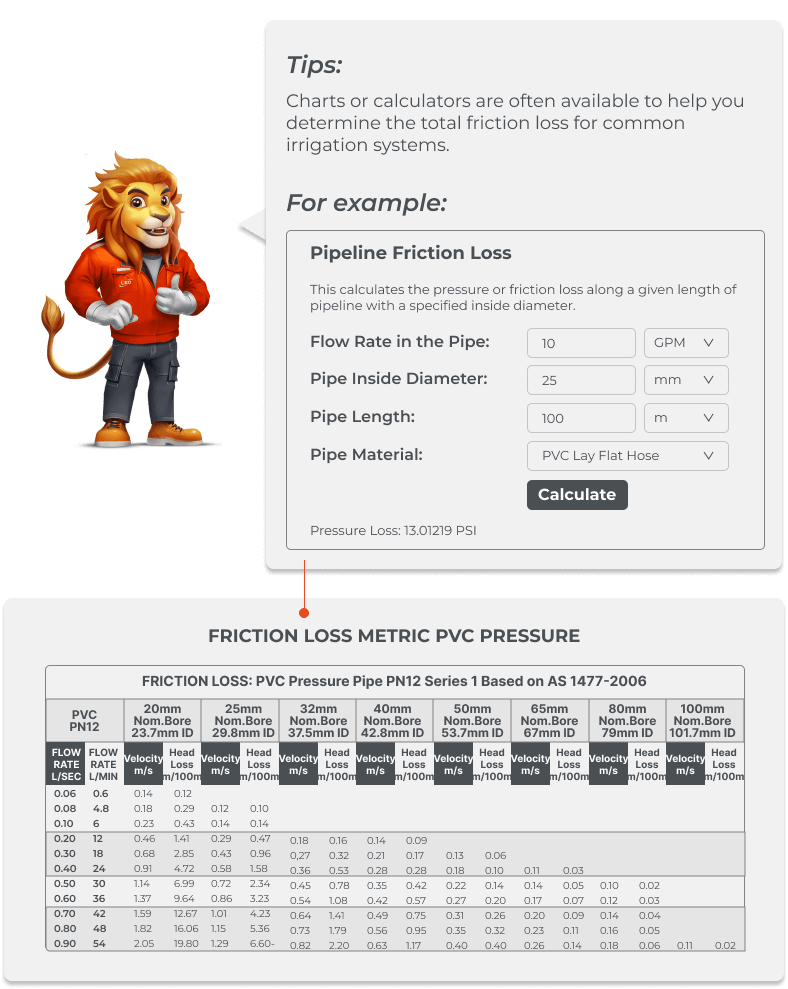
Friction Loss: Pressure loss due to turbulence created by water moving through pipes, valves, or fittings.
c. Types of Irrigation Pumps
There are several types of irrigation pumps available, each with its own unique features, benefits and potential drawbacks. The most common are:
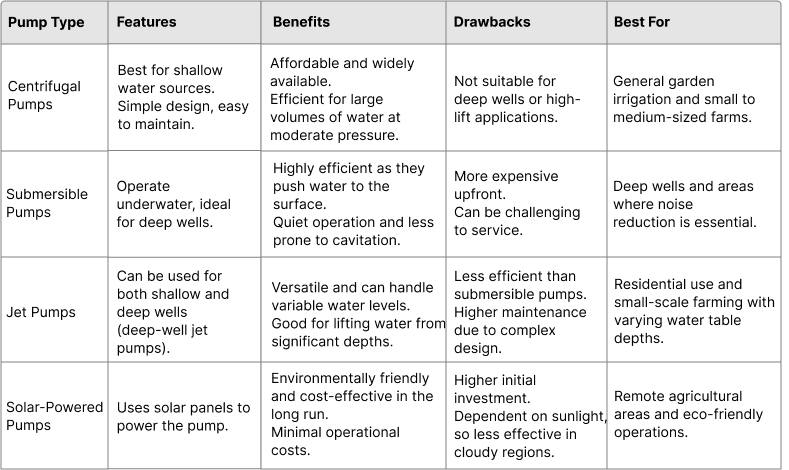
Each type of pump has its specific applications and advantages, so selecting the right one depends on factors such as the flow rate, pressure requirements and the particular needs of your irrigation system.
d. Water Source
The type of water source you have will impact the type of pump you need. Common water sources include:
- Shallow wells
- Deep wells
- Rivers
- Lakes
- Ponds
- Storage tanks
- Municipal water systems
Make it essential to match your water source with the appropriate pump for optimal performance.

e. Other Details Important
Selecting the appropriate pump involves more than just what mentioned. Here are some crucial details to consider:
Power Source: Choose between electricity, petrol or diesel engines, or solar energy based on your location and needs.
Power Supply: Consider the horsepower and voltage requirements.
Pump Location: mounting pad for centrifugal pumps, pump shelter if it will be outdoors.
Maintenance and Durability: Opt for pump designs that are easy to maintain and built to last.
As well as budget, after-sale service, operation cost, etc.
Carefully evaluating these elements will help you select a pump that meets your requirements and provides reliable performance.
Seven Major Steps for Selecting and Sizing an Irrigation Pump
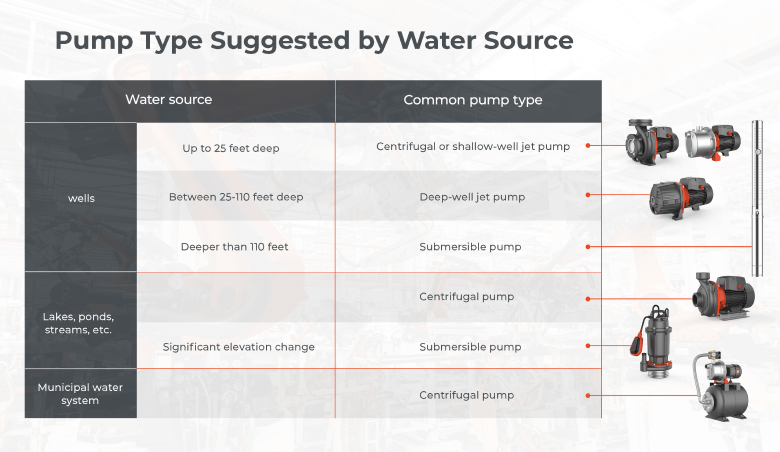
Step 1: Confirm the Right Type of Pump
To select the ideal pump for your irrigation needs, start by determining the type of water source you have. The choice of pump - whether it’s a centrifugal, submersible, or jet pump - depends on factors such as water depth, flow rate, and source type. Matching the pump type to your specific water source ensures optimal performance and efficiency in your irrigation system.
There is a simple guide chart for easier confirmation pump type for your irrigation.
Step 2: Determine the Water Requirements
To ensure your irrigation pump meets your needs, you need to determine your water requirements. Here are two approaches for your reference:
A. Calculate Specific Needs: If you have detailed knowledge of your irrigation needs, list the following:
- Crop Water Needs per Day (CWN): The amount of water the crop requires daily.
- Total Daily Water Requirement (TWR): The total gallons of water needed per day.
- Irrigation Operation Time per Day (IOT): The number of hours the system will run each day.
B. Review System Documents: If you have access to system documentation, check the gallons per minute (GPM) specifications and add them up to determine your total water requirement.
Step 3: Calculate the Flow Rate
Flow rate: for Irrigation system, measured in gallons per minute (GPM)
A: Determine the Required GPM: Assess your irrigation system’s needs and finalize the required gallons per minute.
GPM = TWR/IOT/60
B: Verify the Flow Rate: ensure that it’s GPM
Accurate flow rate calculation helps you select a pump that provides the right amount of water for your irrigation system.
Step 4: Confirm the Pressure Requirements
Assess Required Pressure (PSI): Identify the pressure needed at all entry points of your irrigation system.
Evaluate Elevation Change (Static Head): Measure the vertical distance between the water source and the highest point in the irrigation system.
Account for Friction Losses: The loss of pressure due to friction in the pipes.
Suction Lift: Assess vertical distance between water level and pump inlet if the pump will be installed.
Step 5: Calculate the Pressure
To ensure your pump can handle your irrigation system’s pressure demands for optimal performance, calculate the Total Dynamic Head (TDH).
TDH = Suction Lift + Elevation Change (Static Head) + Friction Loss + Required PSI

Step 6: Confirm the Pump Meet the Flow and Pressure
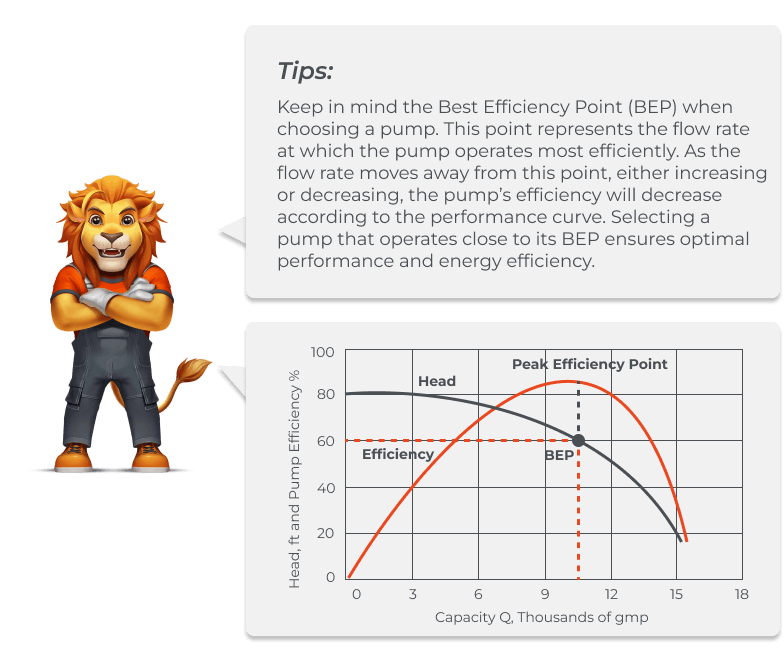
To ensure you select the right pump, review the manufacturer’s performance curves. These curves show how well a pump performs at different flow rates and pressure levels. Match the pump’s capabilities to your required gallons per minute (GPM) and Total Dynamic Head (TDH) to confirm it meets your system’s needs. This step ensures you choose a pump that delivers optimal performance and efficiency for your irrigation setup.
Step 7: Compare and Choose the Best Pump
To select the most suitable pump for your needs, finally you shall consider completely:
Compare Performance: Review different pumps based on their performance curves to ensure they meet your required flow rate and pressure.
Check Efficiency: Opt for pumps that operate close to their Best Efficiency Point (BEP) to maximize energy savings and performance.
Evaluate Features: Consider additional factors like ease of maintenance, durability, and warranty.
Confirm Power Source: Ensure the pump’s power source matches your setup—whether it’s electricity, petrol or diesel engines, or solar energy.
Verify Power Supply: Check that the horsepower and voltage specifications align with your requirements.
Assess After-Sale Service: Look into the support and service options available.
Consider Operating Costs: Factor in the long-term operational costs.
Stay Within Budget: Choose a pump that fits your financial constraints.
Careful consideration of these factors will help you select a pump that delivers reliable, efficient, and cost-effective performance.
Practical Example: Selecting and Sizing an Irrigation Pump
Choosing the right irrigation pump is critical for efficient water delivery and optimal irrigation. Here's a practical example to guide you through the process.
Scenario:
We are irrigating a field of 10 acres of corn, which typically requires 0.25 inches of water per day, 8 hours per day irrigation time.
The required pressure of irrigation system is 30 PSI for optimal operation.
Elevation Change (Static Head) is 50 feet
Friction losses in the pipes are estimated to be 20 feet.
Water Source Assessment:
Type: Well
Quality: Clean and free of large debris
Capacity: Adequate to supply the required water consistently
Additional demands:
Looking for Pump Quality: Durable and energy-efficient pumps are preferred.
Constants
27,154gallons/acre-inch
2.31feet/PSI, 0.433PSI/feet, 0.3048 meter/ feet
1/4.40m3/H/GPM
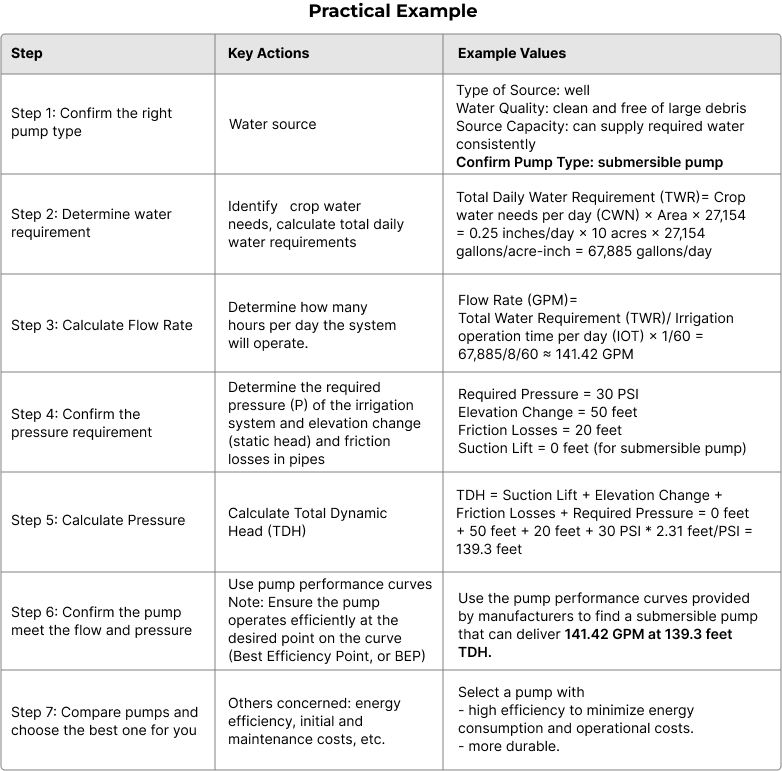
Regarding the step 6, let’s make it understood by our LEO submersible pump.
For this project, to ensure the best performance of the LEO submersible pump, we require a flow rate of 141.42 GPM at a Total Dynamic Head (TDH) of 139.3 feet, equivalent to approximately 32.15 m³/h at 42.46 meters. Upon reviewing the performance curves for the 6XRS30 and 6XRP30 models, we identified two pumps that meet the necessary flow and pressure criteria:
- 6XRS30/6-5.5
- 6XRP30/6-5.5
Both pumps operate near their Best Efficiency Point (BEP) at the specified conditions. Upon further analysis, the 6XRS30/6-5.5 emerged as the more durable option, aligning more closely with our overall requirements. Therefore, we recommend selecting the 6XRS30/6-5.5 for this application.
Conclusion
Choosing the right irrigation pump is essential for the success of your irrigation system. By taking the time to carefully consider your specific needs and requirements, you can make an informed decision that will help you ensure the efficiency and effectiveness of your irrigation efforts for further better crop productivity.
Review the Conclusion Checklist to Better Applying
To ensure the best application of your irrigation pump, review the conclusion checklist thoroughly. Carefully considering all aspects of your specific needs will lead to a more efficient and effective irrigation system.

Thank you for taking the time to read this article. We hope it has provided clarity on how to choose and size an irrigation pump. For further assistance or personalized recommendations, kindly contact our expert team.
Hot Media


LEO at Big 5 Global ...
2025.11.27


A Landmark LEO–Al Mo...
2025.12.02


LEO at the 138th Can...
2025.10.22


LEO Pro-Bono Water S...
2025.08.15


LEO PUMP 2024 Annual...
2025.05.14


A New Journey, A New...
2025.03.18


30 Years of LEO: lea...
2025.01.06


LEO at 30: United Th...
2024.12.16


A New Journey, A New...
2024.11.21


Showcasing Innovatio...
2024.10.25


LEO “Growing Forward...
2024.07.19


LEO Expands Global Q...
2024.09.06


LEO in Action: Power...
2024.08.02


LEO Event Highlight ...
2024.06.07


LEO PUMP at IFAT Mun...
2024.04.28


LEO PUMP at 135th Ca...
2024.04.01


LEO PUMP at MCE 2024...
2024.03.06


LEO PUMP at Big 5 Co...
2024.02.20


LEO PUMP at THE BIG ...
2023.11.16


LEO's Key Role in Wi...
2023.11.04


LEO at 134th Canton ...
2023.10.18


LEO PUMP at SNEC PV ...
2023.06.02


LEO Solution of Wate...
2022.09.28


LEO Project - Solar ...
2022.08.31


LEO Flagship Showroo...
2022.06.28


LEO Project on Power...
2022.06.22