Choosing the Perfect Home Water Booster Pump: A Comprehensive Guide
2024.08.28

The low and unstable water pressure can be a daily annoyance, whether it’s a weak shower stream or slow-filling washing machines. It turns household tasks into frustrating chores at the morning and evening peak hours, especially in summer! But there’s a solution that can ensure a reliable water supply with adequate pressure for your needs: home water booster pump.
When installing a home water booster pump, the first step is to choose the right pump. But how do you go about it?
1. You can hire professional engineers who will handle everything for you. This option saves time and effort, especially if you find a reliable expert. However, if the expert isn’t up to the mark, it could lead to significant issues down the line.
2. Alternatively, you can learn about the key factors in selecting and sizing the ideal water booster pump for your home and then make a decision with the support of a service team. This approach requires more time and effort, as you'll need to be involved in most steps to ensure the best outcome. If done successfully, it will provide long-term convenience.

This guide is designed to help you navigate the selection and sizing of the perfect water booster pump for your home. Keep reading to discover how you can make the right decision, making house water pressure woes a thing of the past, elevating your everyday comfort.
Basic Home Water Booster Pump Understanding
a. What is a Home Water Booster Pump?
A water booster pump is a device designed to increase water pressure in your home. It ensures that water flows consistently and forcefully through your faucets, showers, and appliances, even in areas where water pressure might typically be low.

Major Parameters for a Booster Pump
Pump Flow (Q)
Pump flow represents the volume of water a pump can move, typically measured in liters per minute (LPM) or gallons per minute (GPM). This parameter is determined by the specific requirements of the application, such as the number of fixtures and the overall water usage in a household.
Pump Head (H)
The pump head, also known as the discharge or lift head, refers to the maximum height a pump can lift water against gravity, measured in meters (m), Bar, feet or PSI. Essentially, the pump head indicates the power of the pump - the higher the pump head, the greater the pressure the pump can generate.
b. How Does a Water Pressure Booster Pump Work?
The operation of a water pressure booster pump is straightforward yet effective. The pump draws water from the supply line, accelerates it using an impeller, and then pushes it out with greater force, thereby increasing the water pressure. You can image it by a fan, where rotating blades increase airflow.
This boosted pressure ensures that water reaches all areas of your home, even those that are farthest from the main supply or located on higher floors.
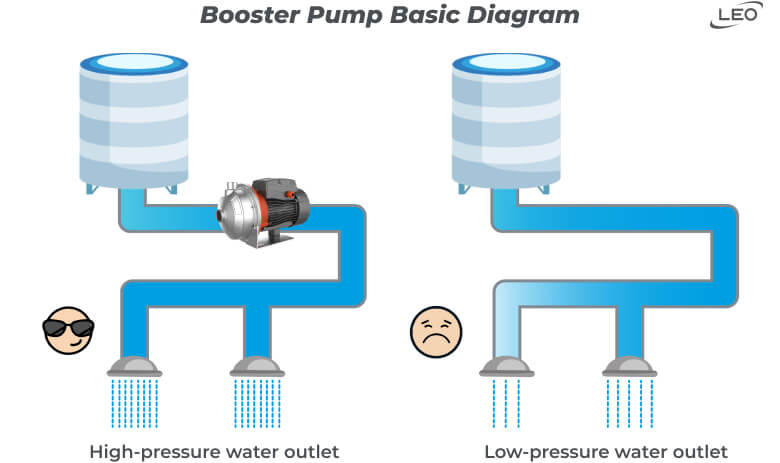
c. Types of Water Booster Pumps for Households
There are several types of home water booster pumps available, each with its own unique features. The most common are:
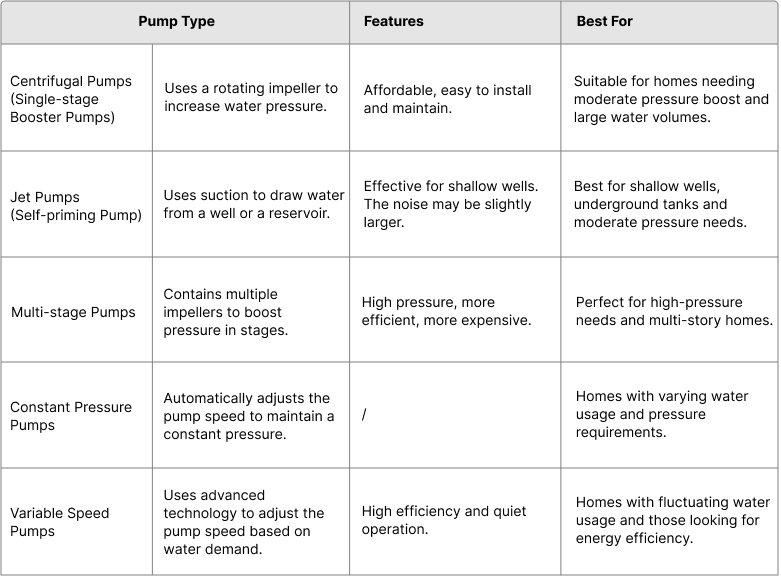
Choosing & Sizing the Perfect Home Water Booster Pump Step by Step
1. Assessing Water Pressure Issues
Low water pressure can manifest in various ways, such as weak showers, slow-filling bathtubs, and ineffective sprinklers. To confirm low water pressure, measure it using a pressure gauge. Attach the gauge to the outdoor spigot closest to where the home's main water supply line enters the house, turn on the water, and read the measurement. Ideal home water pressure is typically between 40-60 PSI (2.76-4.14 Bar).

2. Confirming the Water Source
When selecting booster pump for household applications, understanding the characteristics of various water sources is crucial. Here are the regular water sources and their key characteristics:
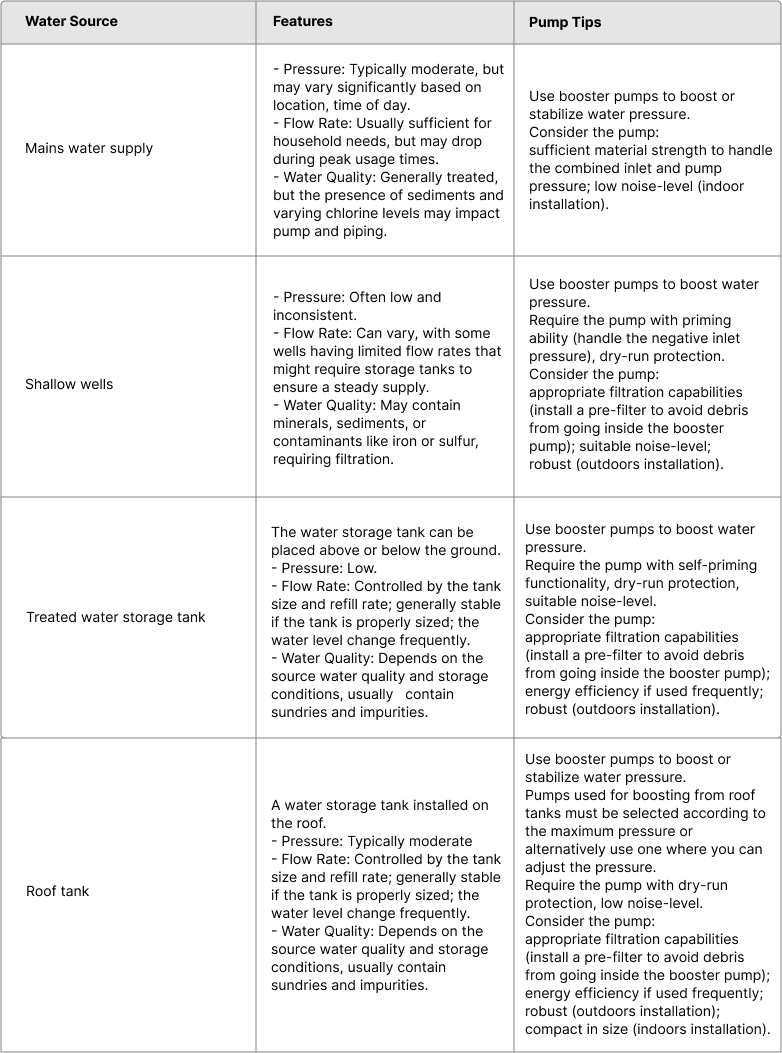
3. Determining Water Usage Requirements
Household Water Demand
Water usage varies based on the number of people and fixtures (sinks, showers, toilets) in a home. For example, a family of four with multiple bathrooms and a washing machine will need more water than a single occupant.
To estimate your household’s water demand, list all water-using appliances and their flow rates. Though there are standard specifications, if you cannot ensure, suggested that confirm yours with the experts (plumbers, manufacturers).

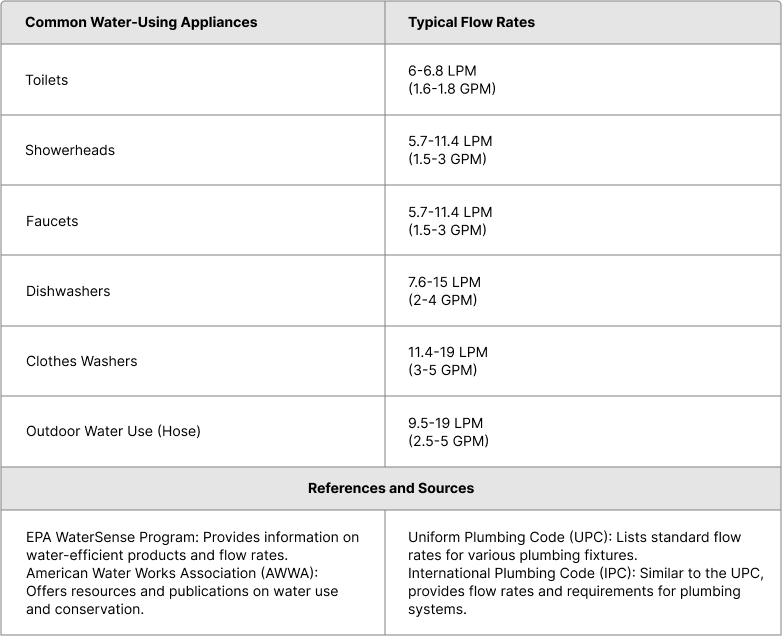
For the most accurate and detailed information, you can refer to the websites of these organizations or their publications. Here are some useful links:
· American Water Works Association
Flow Rate Calculation
To find out how much water you need, calculate the flow rate in liters per minute (LPM). Add up the LPM of all fixtures that might be used simultaneously.
Example: required flow rate = two shower (9 LPM each) + a washing machine (15 LPM) = 33 LPM.
(If you have two showers (9 LPM each) and a washing machine (15 LPM) that might run at the same time, your required flow rate is 33 LPM.)
4. Determine the Required Pump Pressure
Required Water Pressure
As mentioned above, the typical range for household water pressure is between 2.76 to 4.14 Bar (40-60 PSI). And some households may require higher pressure, up to 5.5 Bar, depending on the number of fixtures and the home's size.

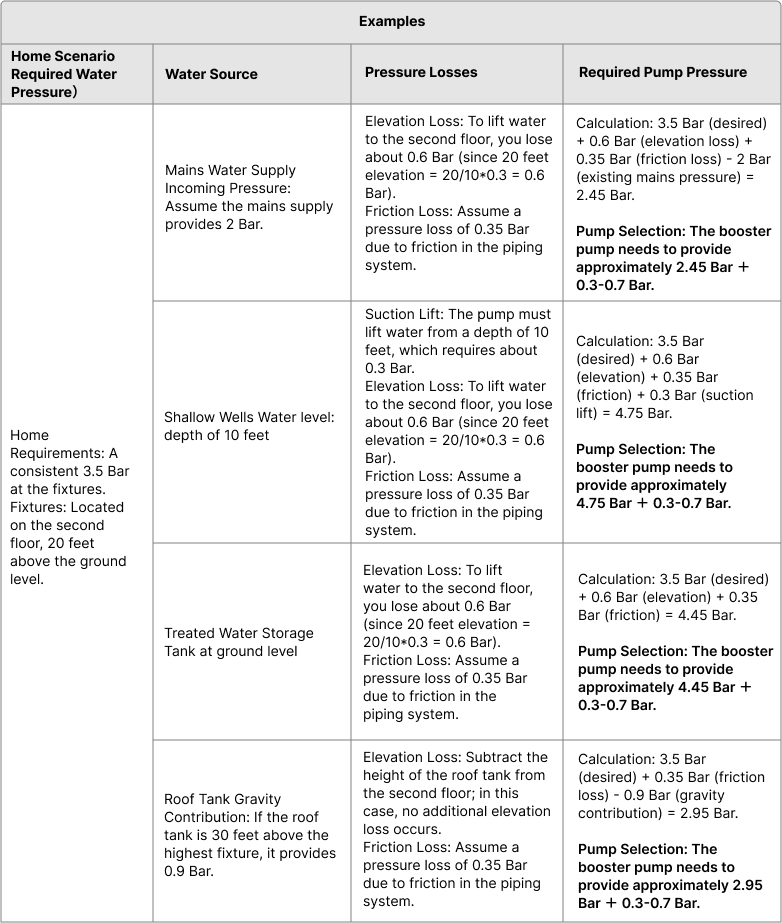
Consider the Pressure Losses
Friction Losses: Account for pressure loss due to friction in the pipes. This depends on pipe length, diameter, material, and the flow rate. Longer or narrower pipes typically result in greater pressure loss.
Elevation Losses: If the water must be pumped to higher floors, calculate the elevation head. For every 10 feet of vertical rise, you lose approximately 0.3 Bar.
Fixture Pressure Requirements: Consider the pressure required at the most demanding fixture or appliance.
Add a Safety Margin
Add a safety margin of 0.3-0.7 Bar to your total required pressure to account for any unexpected pressure drops or future expansions.
Calculate the Pump Pressure
Required Pump Pressure = Required Water Pressure + Friction Losses + Elevation Losses + Fixture Pressure Requirements - Current Water Pressure + Safety Margin
5. Key Factors in Selecting a Water Booster Pump
Confirm the Ideal Pump Type
Identify the most suitable pump types by considering both the water sources and the specific water usage requirements.
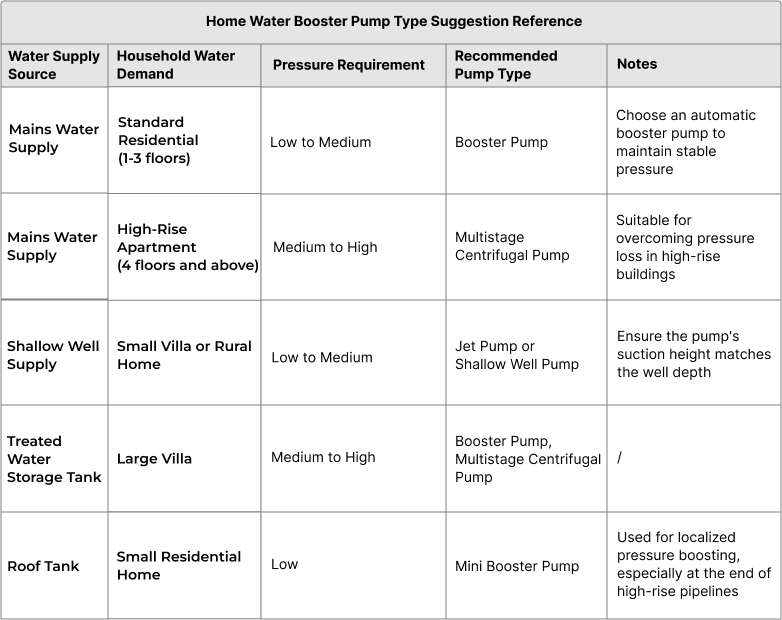
The actual selection should be further optimized based on specific usage environments and technical parameters.
Pump Size and Capacity
Choose a pump that matches your household's flow rate and pressure needs (from Step 3 & step 4). A small pump might not meet high water usage, while an oversized pump can be inefficient.
Energy Efficiency
Energy-efficient pumps can save on electricity bills. Look for pumps with energy-saving features like variable speed drives, which adjust the pump’s power based on demand.
Noise Levels
Consider the noise level of the pump, especially if it’s installed inside the house. Quieter pumps are preferable for residential areas to avoid disturbance.
6. Installation Considerations
Location and Space Requirements
Install the pump in a location with adequate space and ventilation. A typical spot is near the main water line entry point. Ensure there's enough room for maintenance access.
Plumbing Integration
Check the compatibility of the pump with your existing plumbing system. You might need additional components like pressure tanks or check valves to ensure smooth operation.
Electrical Requirements
Ensure the pump has proper electrical supply and safety measures. Hiring a professional for installation can ensure compliance with electrical codes and safety standards.
7. Maintenance and Longevity
Routine Maintenance
Regular maintenance includes checking the pressure, cleaning filters, and inspecting for leaks. Follow the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule to extend the pump’s lifespan.

Troubleshooting Common Issues
Common issues like air leaks or pump cycling can often be resolved with simple fixes. For example, air leaks can be sealed with tape, and pump cycling can be adjusted by checking the pressure settings.
Longevity and Warranty
A well-maintained pump can last for many years. Choose a pump with a good warranty and reliable after-sales support to ensure long-term performance.
8. Cost Considerations
Initial Purchase Costs
Prices vary based on type and capacity. Expect to spend between $200 and $1,000.
Installation Costs
Professional installation might add to the cost but ensures proper setup and safety. Professional installation might cost between $200 and $500.
DIY installation can save money but requires technical knowledge.
Operational Costs
Consider ongoing costs like electricity and maintenance. Such as energy-efficient models might have higher upfront costs but save money in the long run.
Return on Investment
Improved water pressure enhances daily comfort and can add value to your home. The initial investment often pays off through increased efficiency and convenience.
9. Number of Pumps
Determine the number of pumps your whole booster system will utilize. For large homes or villas, especially those with multiple bathrooms and high water usage, installing multiple booster pumps may be necessary to ensure consistent water pressure throughout the property. In contrast, smaller homes or apartments might suffice with a single, well-sized booster pump.

Example: Selecting a Booster Pump for a Residential Villa
Scenario
Select a booster pump for a residential villa that has two floors, four bathrooms, a kitchen, and an irrigation system for the garden. The villa is located in an area where the municipal water pressure is inadequate, and you need to boost the water pressure to ensure sufficient flow to all fixtures.
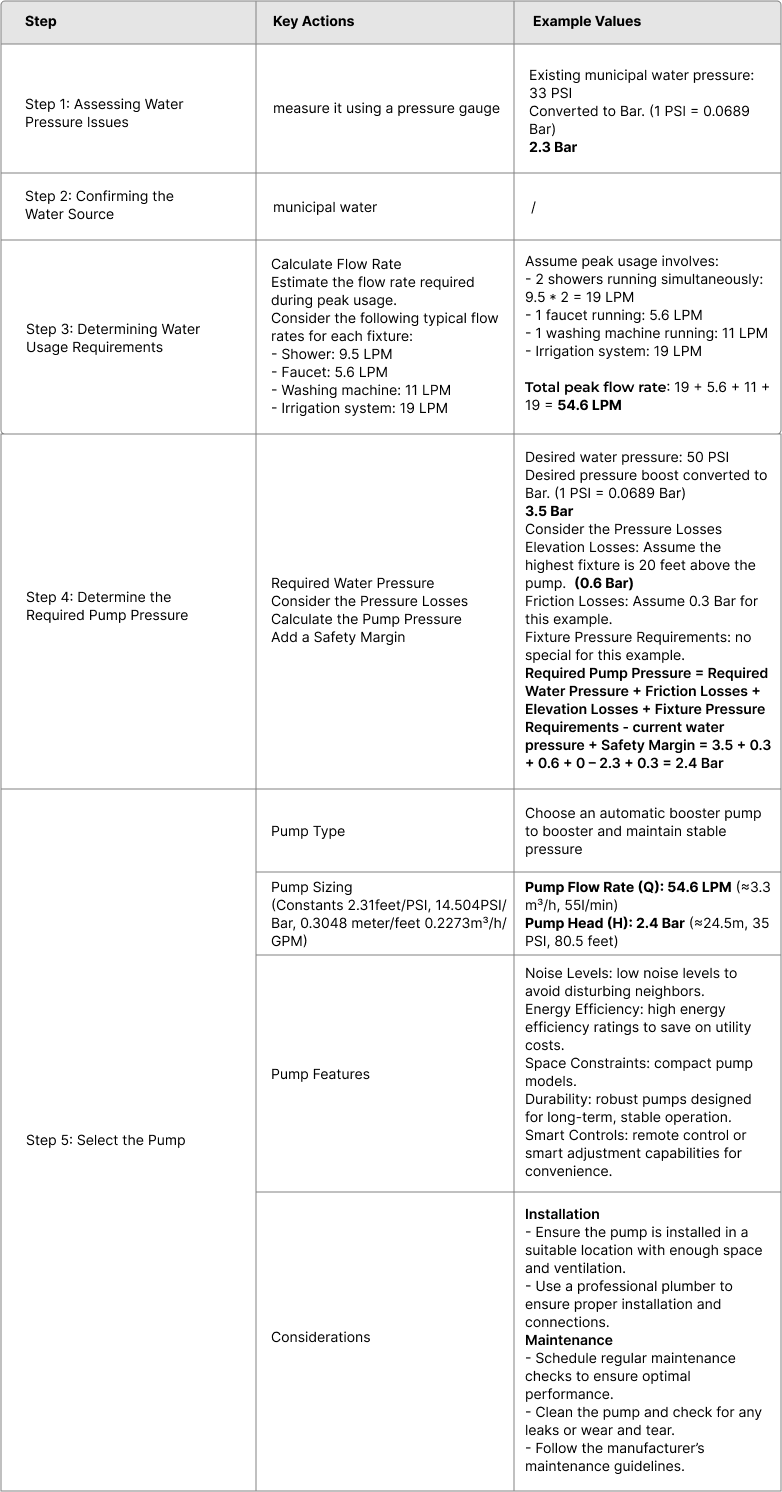
Example Pump Specification
Pump Flow Rate (Q): 54.6 LPM (≈3.3 m³/h, 55l/min)
Pump Head (H): 2.4 Bar (≈24.5m, 35 PSI, 80.5 feet)
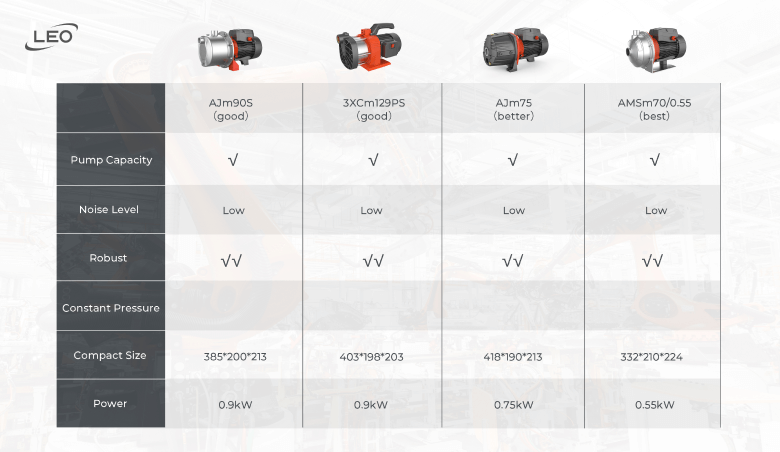
Recommended Pump Model
Conclusion
Selecting and sizing the right home water booster pump involves understanding your water pressure needs, household demand, water sources and the types of pumps available, calculating the water flow and pressure, considering factors like energy efficiency, noise levels, and cost. By holding such ways and consulting with qualified pump specialists when needed, you can make an informed decision that ensures consistent and reliable water pressure in your home.
Rely on LEO Pump for expert advice and a free consultation. With a sales and service network spanning over 160 countries, we're here to assist you in every aspect of domestic water pump selection, maintenance, and warranty. Trust our experience to guide you through the process and ensure you make the best choice for your needs.
Hot Media


LEO at Big 5 Global ...
2025.11.27


A Landmark LEO–Al Mo...
2025.12.02


LEO at the 138th Can...
2025.10.22


LEO Pro-Bono Water S...
2025.08.15


LEO PUMP 2024 Annual...
2025.05.14


A New Journey, A New...
2025.03.18


30 Years of LEO: lea...
2025.01.06


LEO at 30: United Th...
2024.12.16


A New Journey, A New...
2024.11.21


Showcasing Innovatio...
2024.10.25


LEO “Growing Forward...
2024.07.19


LEO Expands Global Q...
2024.09.06


LEO in Action: Power...
2024.08.02


LEO Event Highlight ...
2024.06.07


LEO PUMP at IFAT Mun...
2024.04.28


LEO PUMP at 135th Ca...
2024.04.01


LEO PUMP at MCE 2024...
2024.03.06


LEO PUMP at Big 5 Co...
2024.02.20


LEO PUMP at THE BIG ...
2023.11.16


LEO's Key Role in Wi...
2023.11.04


LEO at 134th Canton ...
2023.10.18


LEO PUMP at SNEC PV ...
2023.06.02


LEO Solution of Wate...
2022.09.28


LEO Project - Solar ...
2022.08.31


LEO Flagship Showroo...
2022.06.28


LEO Project on Power...
2022.06.22